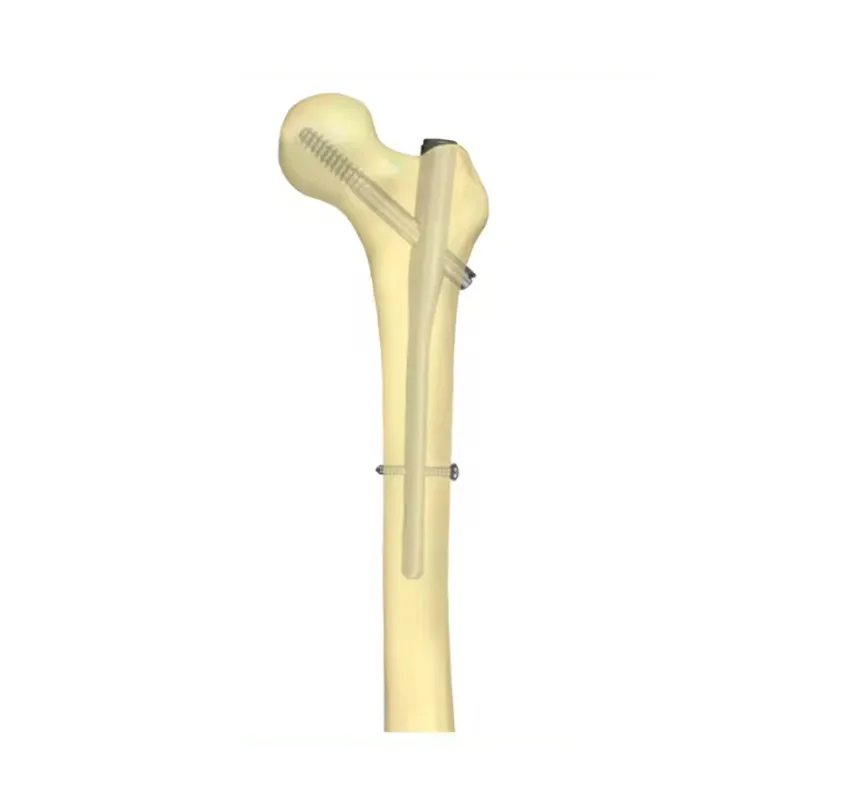
The Role of Titanium Intramedullary Nails in Orthopedic Surgery
In modern orthopedic surgery, the choice of implant materials plays a critical role in patient outcomes, especially in fracture treatment. Intramedullary nails have been widely used to stabilize long bone fractures, and among various options, titanium intramedullary nails have become increasingly preferred by surgeons worldwide. Their unique properties contribute significantly to the effectiveness and success of orthopedic procedures.
This article explores why titanium intramedullary nails are favored in modern orthopedics. It examines their material characteristics, clinical advantages, and how they enhance the fracture healing process. Understanding these factors helps clarify the increasing reliance on titanium intramedullary nails in surgical practice.
Material Advantages of Titanium Intramedullary Nails
Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Titanium is renowned for its excellent biocompatibility, making it an ideal material for implants. When intramedullary nails are inserted into the body, the surrounding tissue must tolerate the material without adverse reactions. Titanium intramedullary nails minimize the risk of inflammation, allergic response, or rejection due to their inert nature.
Moreover, titanium’s exceptional corrosion resistance guarantees that the intramedullary nails maintain their stability inside the body for extended durations. Unlike certain metals that may deteriorate or release potentially harmful ions, titanium preserves both its structural integrity and chemical stability within the physiological environment. This unique property significantly enhances the long-term durability and safety of titanium intramedullary nails, making them a reliable choice for fracture fixation over time.
Lightweight and High Strength
Titanium intramedullary nails uniquely blend lightweight characteristics with outstanding mechanical strength. This balance is essential because implants must be strong enough to withstand the mechanical stresses encountered during everyday movements, yet light enough to avoid impeding the patient’s natural mobility. By achieving this combination, titanium nails provide effective support for fracture healing while allowing patients to regain function with minimal discomfort or restriction.
The lightweight nature of titanium nails significantly lessens the stress exerted on the surrounding bone and soft tissues, which in turn enhances patient comfort and supports earlier mobilization. Simultaneously, the high tensile strength of these nails offers strong and reliable fracture stabilization, minimizing the chances of implant failure throughout the healing process. This combination of lightness and strength makes titanium nails particularly effective in promoting successful recovery while maintaining patient well-being.
Clinical Benefits in Orthopedic Procedures
Improved Healing Environment
The design and material composition of titanium intramedullary nails play a crucial role in creating an ideal environment for bone healing. These nails offer rigid internal support that ensures proper alignment and mechanical stability of the fractured bone. Maintaining this stability is vital for the natural bone regeneration process, as it allows for effective biological repair while minimizing the risk of malunion or delayed healing. The combination of precise design and durable titanium material helps facilitate a smoother and more reliable recovery.
Moreover, titanium’s biocompatibility supports osseointegration—the process where bone cells grow and bond to the implant surface. This biological integration promotes faster and stronger healing compared to materials that do not encourage such interaction. As a result, titanium intramedullary nails enhance patient recovery outcomes by facilitating stable and efficient bone repair.
Reduced Risk of Implant-Related Complications
Postoperative complications are a significant concern in orthopedic surgeries. Titanium intramedullary nails help minimize such risks due to their favorable material properties. The reduced likelihood of allergic reactions and infections makes titanium nails a safer option for diverse patient populations.
Furthermore, titanium’s resistance to corrosion and wear decreases the chances of implant degradation, which can lead to implant loosening or failure. This reliability is critical in complex or long-term fracture management, ensuring sustained support throughout the recovery process.
Technical Considerations and Surgical Application
Ease of Implantation and Surgical Precision
The use of titanium intramedullary nails supports minimally invasive surgical techniques. Their design allows for insertion through small incisions, reducing tissue trauma and improving cosmetic outcomes. Surgeons can precisely position the nails using advanced imaging and navigation tools, which improves fixation accuracy.
The compatibility of titanium nails with various locking mechanisms enhances fracture stabilization. Surgeons can tailor the fixation according to fracture type and patient anatomy, optimizing the mechanical environment for healing.
Versatility Across Different Fracture Types
Titanium intramedullary nails are highly versatile, suitable for a range of long bone fractures including femur, tibia, and humerus fractures. Their adaptable designs accommodate simple to complex fractures, including comminuted and segmental types.
This versatility reduces the need for multiple implant systems and simplifies surgical decision-making. Patients benefit from a treatment option that addresses their specific fracture characteristics while promoting efficient recovery.
Future Developments and Innovations
Advances in Titanium Implant Technology
Research continues to enhance the performance of titanium intramedullary nails. Innovations include surface treatments that improve osseointegration, antibacterial coatings to reduce infection risk, and modifications to nail geometry for better anatomical fit.
These advancements aim to further improve clinical outcomes and expand the applications of titanium nails in orthopedic trauma care. Enhanced implant design and material science contribute to evolving standards in fracture treatment.
Integration with Digital Surgery Tools
The integration of titanium intramedullary nails with digital surgical tools is another promising development. Computer-assisted navigation and robotic systems allow surgeons to plan and execute implant placement with high precision.
This technological synergy improves the accuracy of titanium nail insertion, reduces operative time, and minimizes complications. As digital surgery becomes more prevalent, titanium intramedullary nails remain at the forefront of implant technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes titanium intramedullary nails superior to other materials?
Titanium intramedullary nails offer superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and a favorable strength-to-weight ratio. These properties enhance patient safety, comfort, and implant durability compared to alternative materials.
Are titanium intramedullary nails suitable for all patients?
Titanium nails are suitable for most patients with long bone fractures. However, individual patient factors and fracture characteristics influence the choice of implant. Surgeons assess these aspects before recommending titanium nails.
How does titanium affect the healing process?
Titanium supports osseointegration, allowing bone cells to bond directly to the implant. This biological interaction promotes faster and stronger healing compared to non-biocompatible materials.
What are the risks associated with titanium intramedullary nails?
Risks are generally low but can include infection, implant loosening, or mechanical failure. Proper surgical technique and patient management minimize these risks.
 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 AR
AR