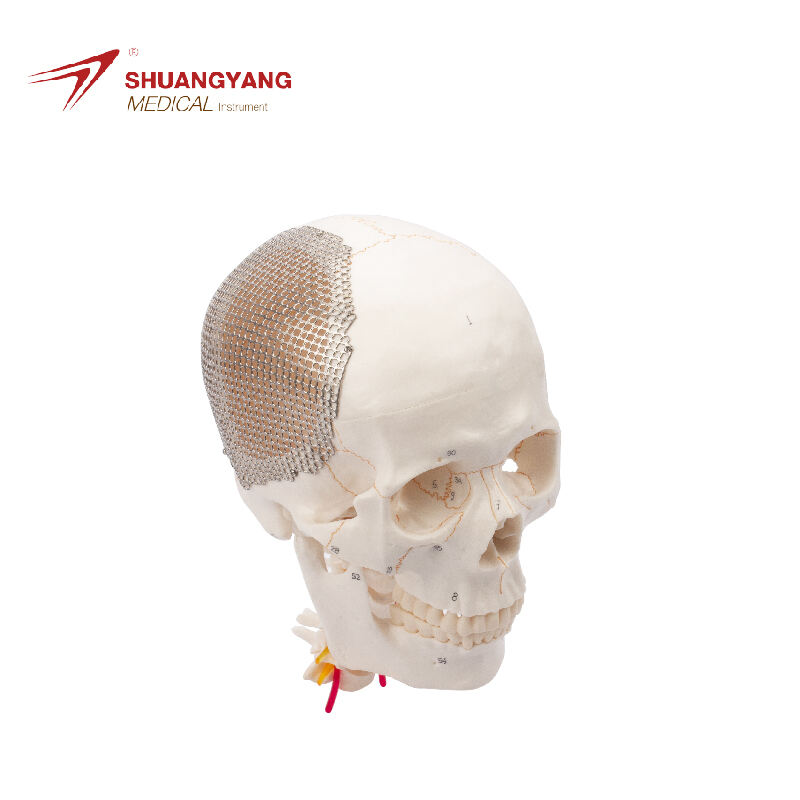
skull
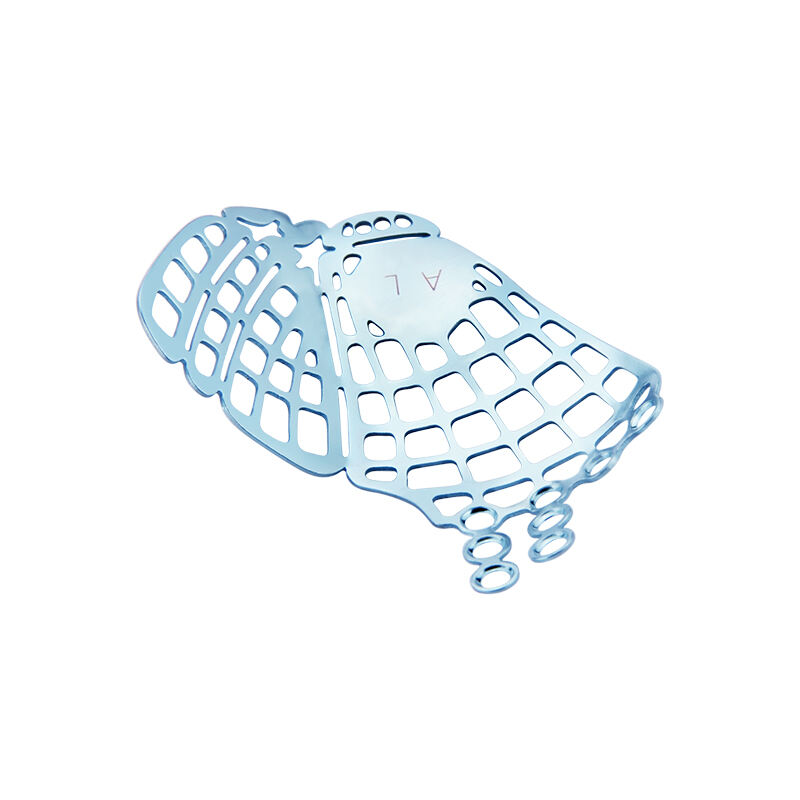
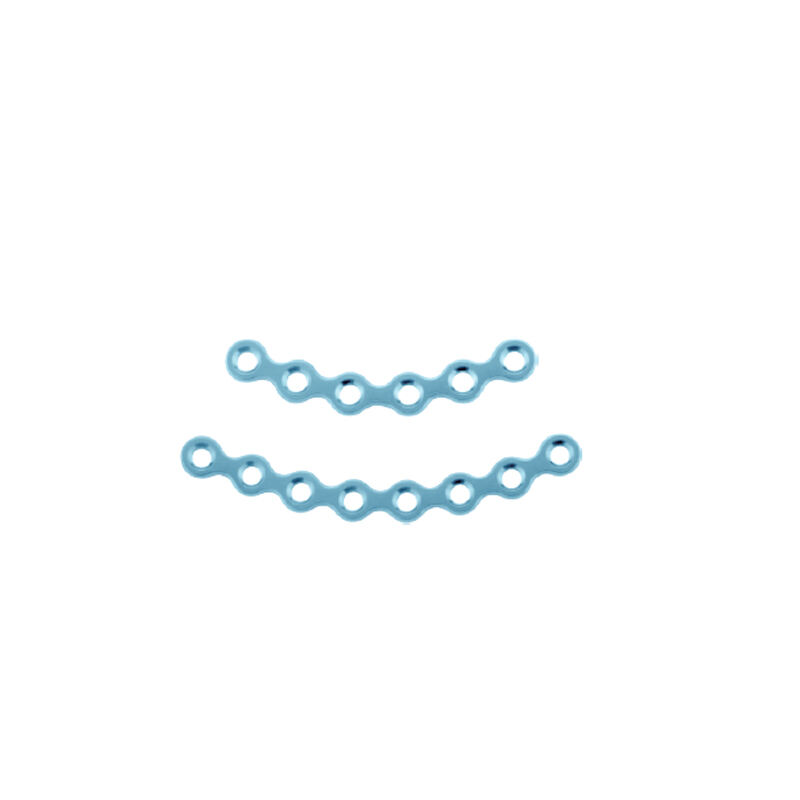
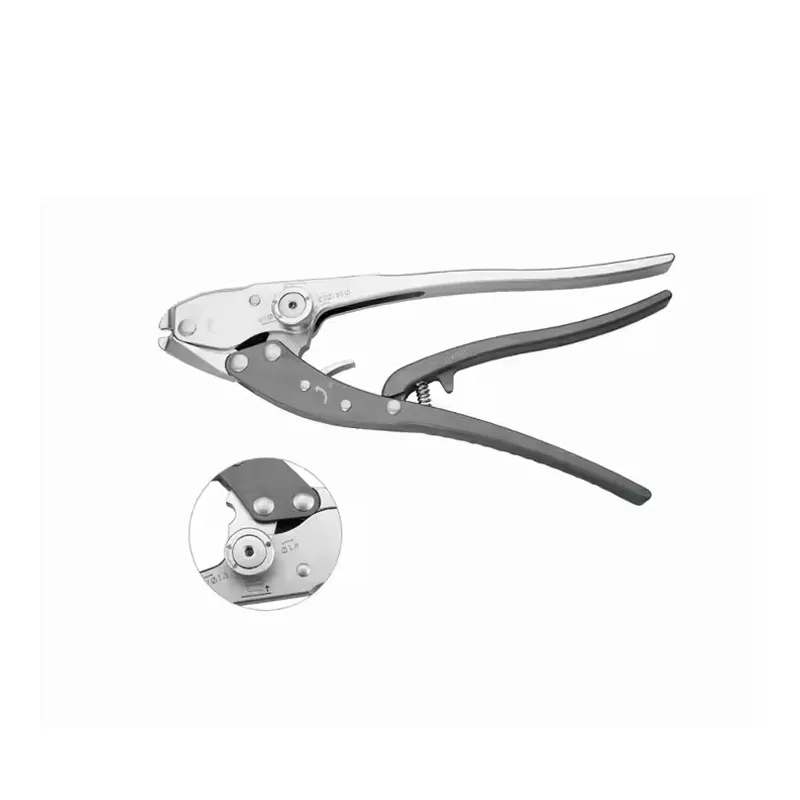
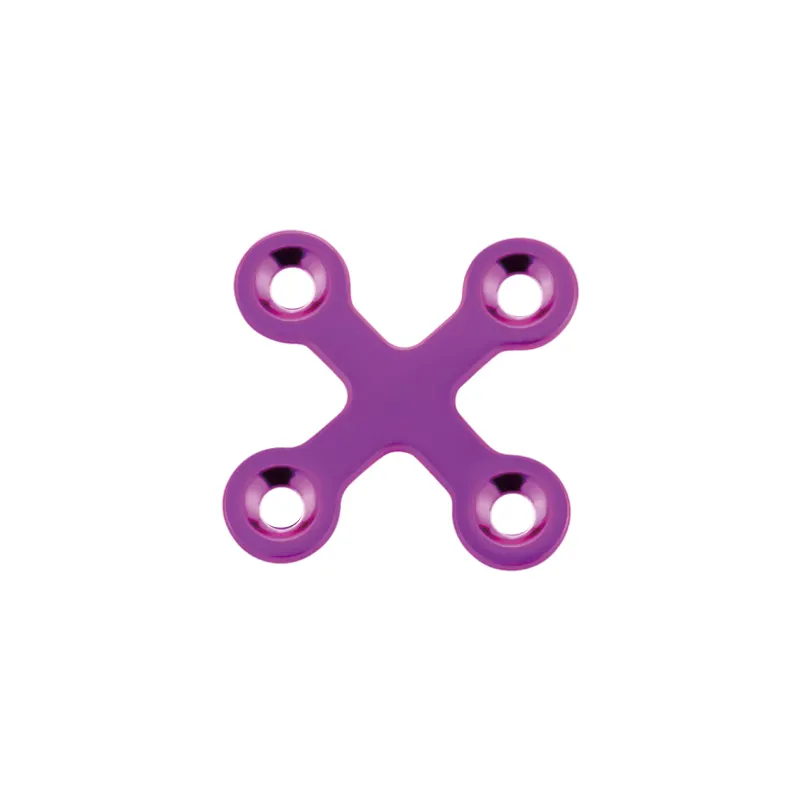
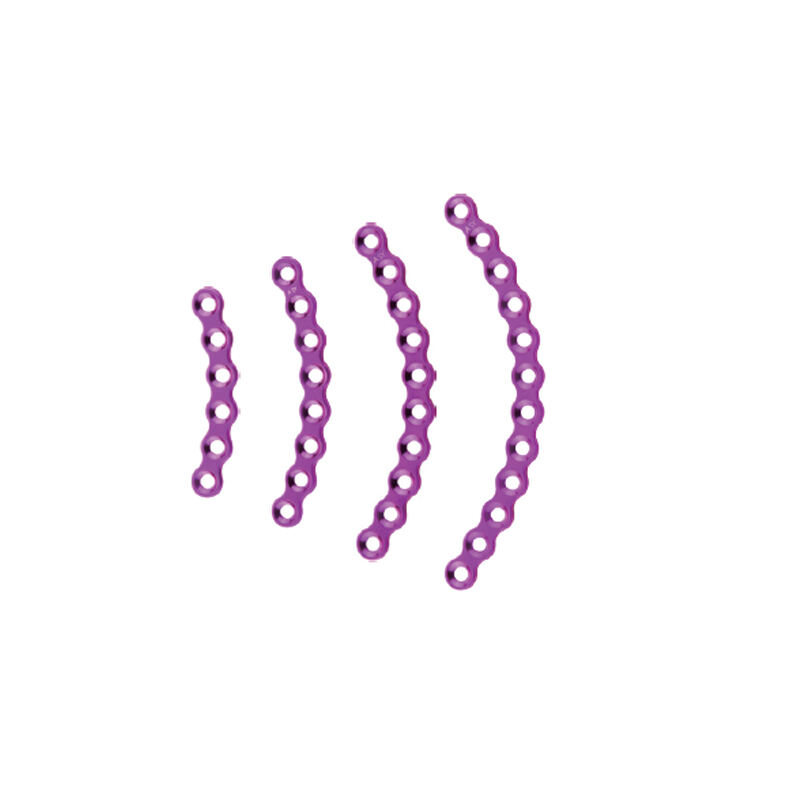
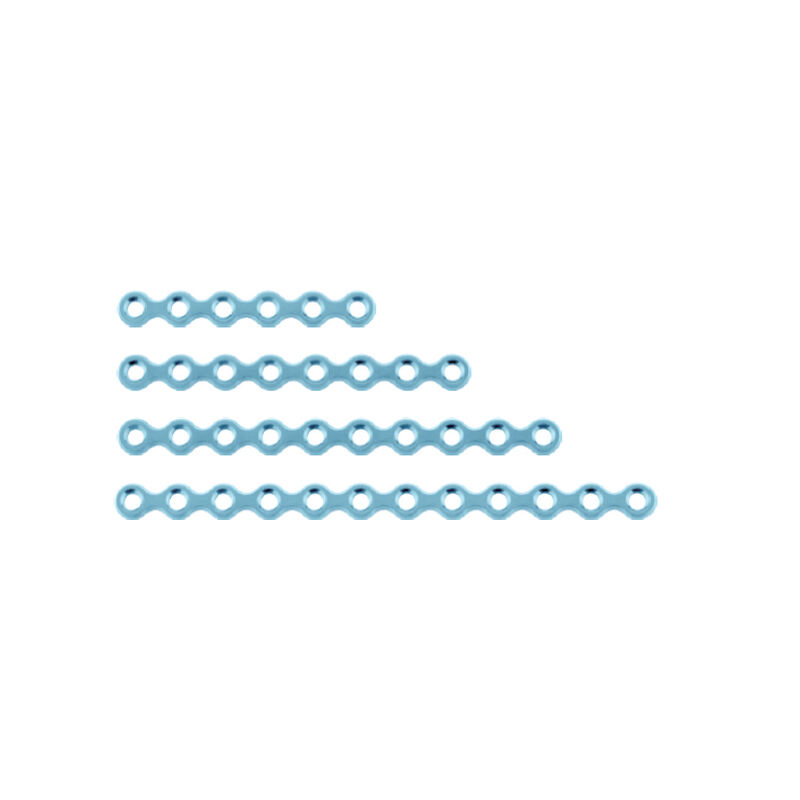
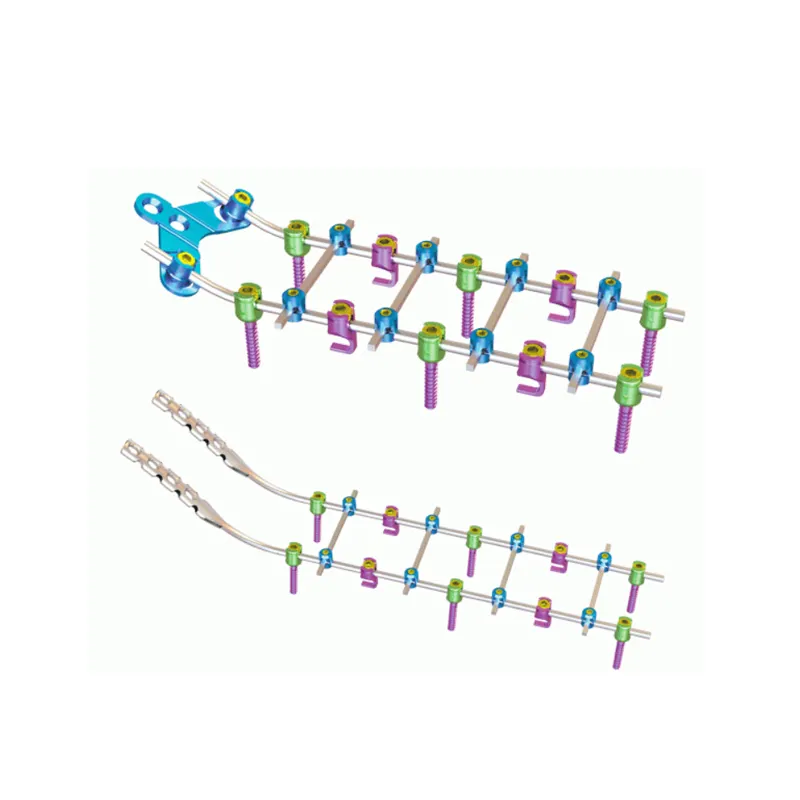
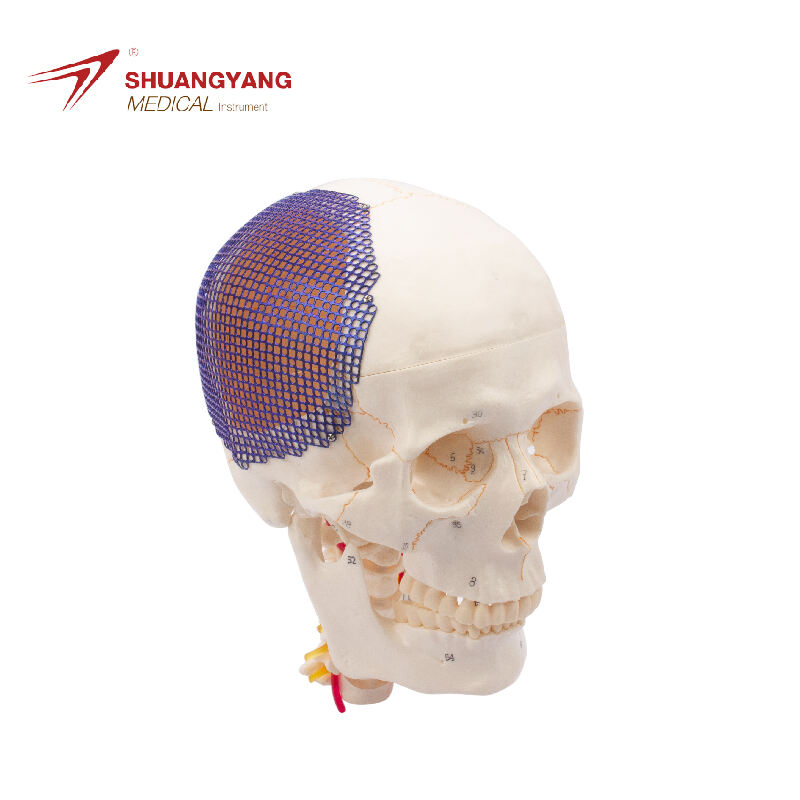
The skull is the bony structure that forms the head in vertebrates, including humans. It is composed of 22 bones and serves as the primary protection for the brain, housing the brain and supporting the face. The main functions of the skull include safeguarding the brain from injury, providing a structure for the attachment of muscles, and serving as the point of attachment for the first two cervical nerves. Technological features of the skull involve its unique architecture, which combines strength with lightness, allowing for durability without impeding movement. In medical and health applications, the skull is crucial for craniotomy procedures and is studied extensively in forensics and anthropology to understand human evolution and identify remains.
 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 AR
AR