Shuangyang Building, Yangshe Town, Zhangjiagang City, Jiangsu Province, China.
Shuangyang Building, Yangshe Town, Zhangjiagang City, Jiangsu Province, China.
Our maxillofacial implant products:
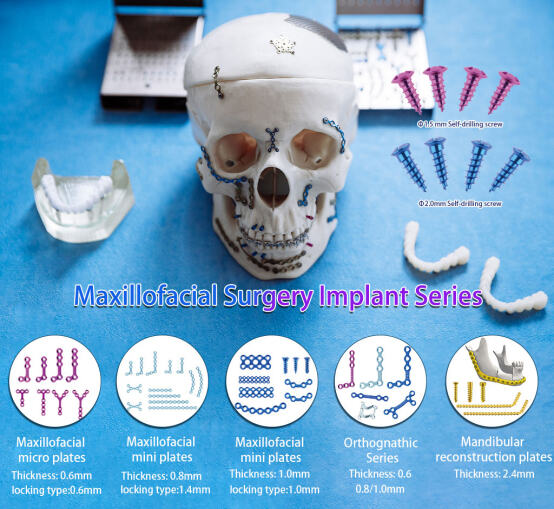
Maxillofacial Internal Fixation System:
Based on the existing consensus of medical anatomy, our current range of maxillofacial products encompasses the following areas:
I. Bone structure area
1. Maxillary region: constitutes the skeleton of the middle part of the face, participates in the formation of the orbital floor, the roof of the oral cavity and the lateral wall of the nasal cavity, and contains the maxilla, zygomatic bone, nasal bone and palatine bone, etc.
I I.Mandibular region: the only movable bone of the face, supporting the lower rows of teeth and participating in the temporomandibular joint formation.
Zygomatico-orbital region: covers the zygomatic bone, infraorbital rim and part of the frontal bone, constituting the outer contour of the face.
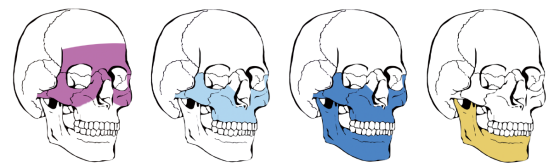
I. Elements of trauma diagnosis
Asphyxia control: Immediate removal of foreign objects from the mouth and nose, tongue retraction and immobilisation if tongue is falling back, tracheotomy if necessary (cricothyroid puncture is an emergency measure).
Bleeding control: compression of the branches of the external carotid artery (superficial temporal artery, external maxillary artery), deep wounds filled with haemostatic powder/gelatin sponge.
Comorbid injury screening: prioritise craniocerebral injury (history of coma, cerebrospinal fluid leak), cervical spine fracture and cervical macrovascular injury.
(2) Specialist examination
1.Palpate for bone continuity (orbital rim, zygomatic arch, mandible) and observe for occlusal malocclusion (core indications for jaw fracture).
2.Diagnostic confirmation: skull X-ray film initial screening, CT scan to clarify the direction of the fracture line and the degree of displacement (especially mid-facial compound fracture).
1.Transmural function (presence or absence of facial paralysis), sensory abnormalities in the trigeminal distribution.
2.Injury (parotid duct rupture causing salivary fistula), ocular motility disorders (orbital wall fracture).
(3) Infection risk identification
II. Restorative treatment strategies
(1) Soft tissue repair
Layered suturing: precise alignment of mucosa, muscle and skin, hard palate tear closed with mucoperiosteal sutures.
Organ reimplantation: haemoreduction of isolated tissues (lip, nose, ear) within 6 hours with hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Nerve/duct repair: microanastomosis of facial nerve, parotid duct reconstruction against salivary fistula.
(2) Reconstruction of bony structures
Technology Type |
Applicable Scenarios |
Technical Advantages |
Internal fixation with titanium plates |
Linear fractures (mandible, zygoma) |
Stability and early functional training |
3D printed customised restorations |
Extensive defects (post tumour surgery, comminuted fractures) |
Precise matching of anatomical patterns |
Vascularised fibula graft |
segmental mandibular defect |
Excellent biocompatibility and long-lasting support |
For maxillofacial fixed titanium plates we have a complete set
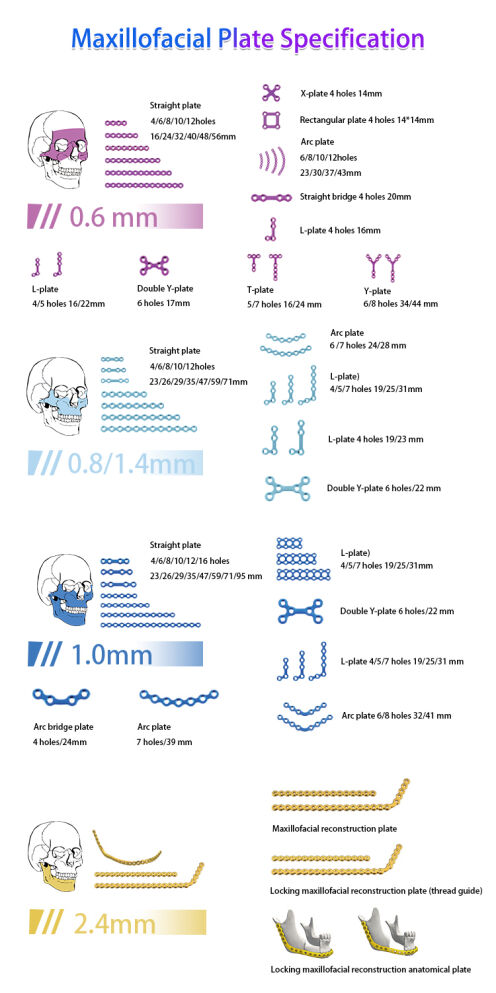
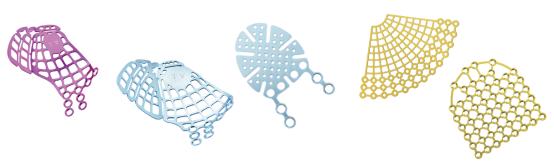
(3) Application of minimally invasive techniques
Endoscopic assistance: transoral approach to reset condylar fractures to avoid facial scarring and facial nerve damage.
Digital navigation:
Pre-operative 3D modelling to simulate the extent of osteotomy and printing of individualised guides (error <0.5mm).
Pre-bending of the reconstructed titanium plate reduces the operating time by 20%.

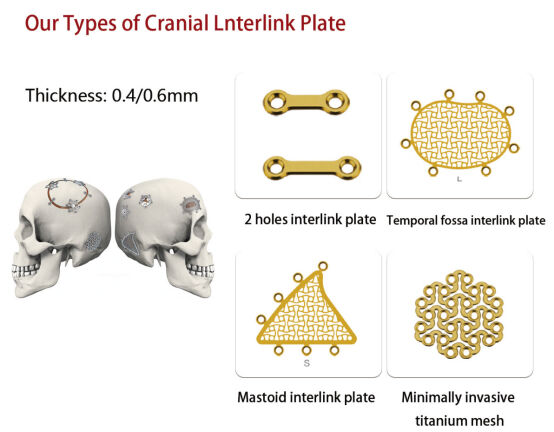
III. Management points during surgery
Anti-infection: prophylactic antibiotics to cover oral flora, early closure of sinus cavity traffic wounds .
Nutritional support: nasal feeding/soft food to avoid masticatory load, maintain moist oral environment.
Functional rehabilitation: mouth opening training to prevent joint ankylosis, occlusal plate to adjust occlusal relationship.
IV. Trends in technological evolution
Biomaterial innovation: polyether ether ketone (PEEK) composite implants promote osseointegration.
Intelligent Surgical System: AR navigation to locate fracture breaks in real time and enhance the precision of complex reconstruction.
In the long river of science and technology of bone repair, shuangyang medical treatment always takes the times as the ruler and the needs as the anchor. Facing the global trend of aging wave and precision medicine, we continue to reform and innovate, and every innovation begins with the deep listening to clinical pain points and ends with the real improvement of patients' quality of life.
In the future, we will continue to adhere to the manufacturing philosophy of ‘millimetre precision, billion-tonne responsibility’, so that global orthopaedic solutions not only keep up with the market, but also lead the demand; so that implants are not only a combination of metals, but also a token of regaining freedom of movement. Because of the belief that the only eternal competitiveness through the cycle is to cast human health into the product gene.’