sternum
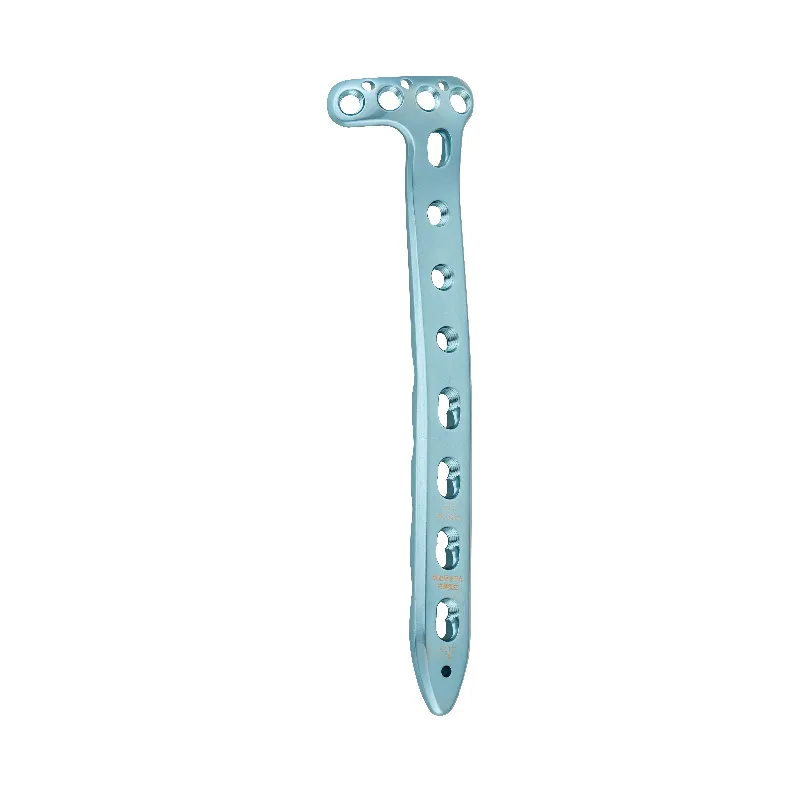
The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a flat bone that forms the front of the rib cage in humans. It plays a pivotal role in the skeletal system with several main functions. The primary function of the sternum is to protect vital organs in the chest, such as the heart and lungs, by acting as a shield. Structurally, it provides an anchor point for the ribs and forms the middle of the Thoracic skeleton, contributing to the stability of the chest wall. Technological features of the sternum include its unique shape and structure, composed of three parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. In medical applications, the sternum is essential in various surgical procedures, including median sternotomy, where the bone is cut to access the heart and lungs. Additionally, it serves as a reference point for medical examinations and treatments.
 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 AR
AR